Basic information
- Phenotype
- CTNNB1 mutation
- Description
- Somatic non-synonymous mutation in CTNNB1 compared to samples without a non-synonymous mutation.
- Method
- Somatic mutations were converted from the genome assembly hg38 to hg19 by CrossMap (version 0.5.3). Unmapped mutations were excluded from downstream analysis. MutSigCV (version 1.41)was applied to the converted somatic mutations to identify significantly mutated genes (q value < 0.01) for each cancer type. Synonymous mutations were not included. The default reference files, background coverage (exome full192), mutation types, and gene covariates, were used in this analysis.
Gene association
Number of significant genes with P-value ≤ 10-6 for each cohorts are summarized in bar plots. The scatter plot highlights significant associations diven by protein rather than mRNA abundance.
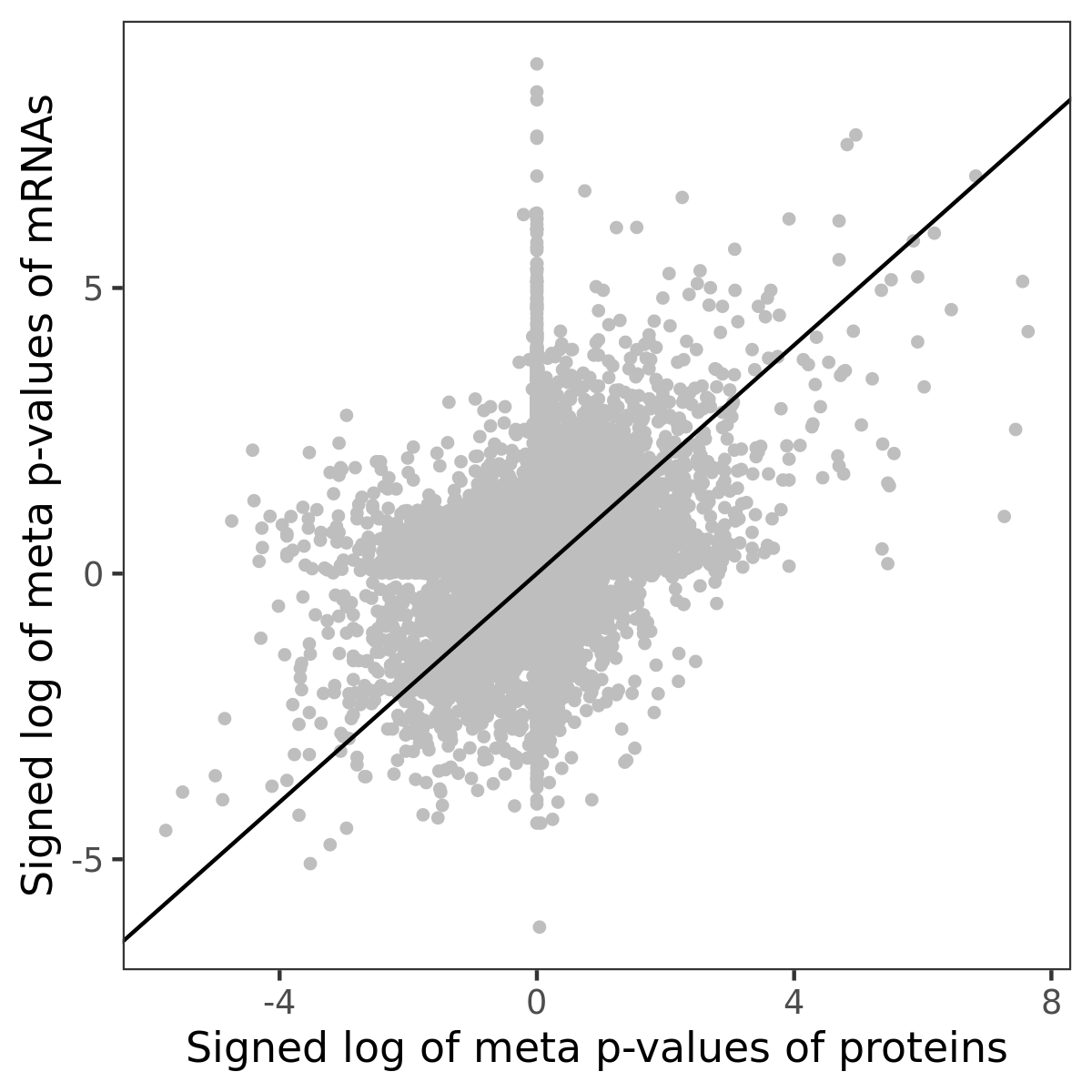
Association of protein abundance of genes
| Signed p-values | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Meta P | BRCA | CCRCC | COAD | GBM | HNSCC | LSCC | LUAD | OV | PDAC | UCEC |
Gene set enrichment analysis
Submit genes and the common logarithm of the p-values of their association with CTNNB1 mutation to WebGestalt.
Phosphosite association
Number of significant genes with P-value ≤ 10-6 for each cohorts are summarized in the bar plot. The scatter plot highlights significant associations diven by phosphorylation rather than protein abundance.
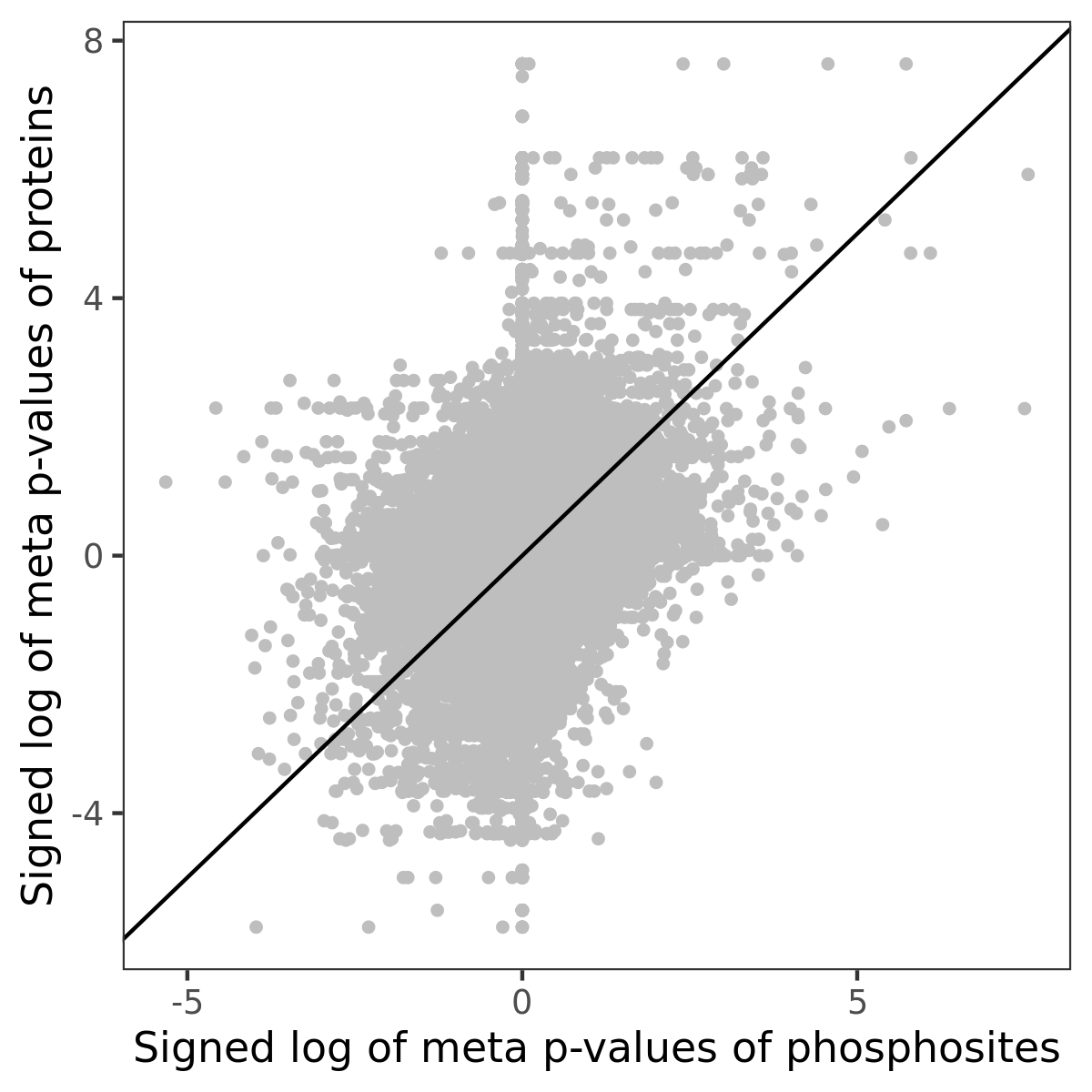
| Signed p-values | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Protein | Site | Meta P | BRCA | CCRCC | COAD | GBM | HNSCC | LSCC | LUAD | OV | PDAC | UCEC |
Gene set enrichment analysis
Submit phosphorylation sites and the common logarithm of the p-values of their association with CTNNB1 mutation to WebGestalt.